我们都知道
SpringBoot自问世以来,一直有一个响亮的口号"约定优于配置",其实一种按约定编程的软件设计范式,目的在于减少软件开发人员在工作中的各种繁琐的配置,我们都知道传统的SSM框架的组合,会伴随着大量的繁琐的配置;稍有不慎,就可能各种bug,被人发现还以为我们技术很菜。而SpringBoot的出现不仅大大提高的开发人员的效率,还能避免由于"手抖"带来的配置错误。
很多程序员都感慨SpringBoot的到来大大解放了生产力,但是也有聪明的程序猿会多思考一下下,SpringBoot是怎么做到的约定的配置?它配置在了哪里?又是怎么启动的作用等等一系列的问号在跟女朋友花前月下的时候,依然会时不时冒出来。这严重影响了程序猿们的"幸"福生活,为了能广大"程序猿"同胞过上幸福美满的生活,今天咱么就来一起跟随源码探究下SpringBoot到底是如何做到"约定优于配置"的。
首先,我们先介绍下我们的演示的项目环境,我们先试用 Spring Initializr来创建一个SpirngBoot 工程。我们使用的版本是SpringBoot 2.4.3.RELEASE 
接下来就只在 pom.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>这样我们的环境就准备好了。
我们跟着 SpringBoot的源码来探究它的启动流程,首先,先找到这个应用程序的入口主方法,在上面打一个断点: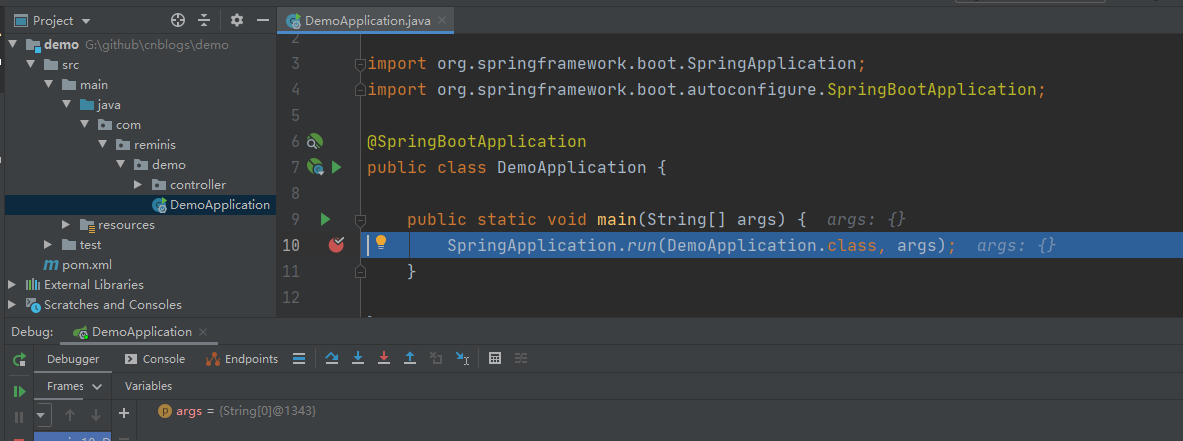
启动之后,F7进入到 run()方法,我的电脑是点击F7(Step into)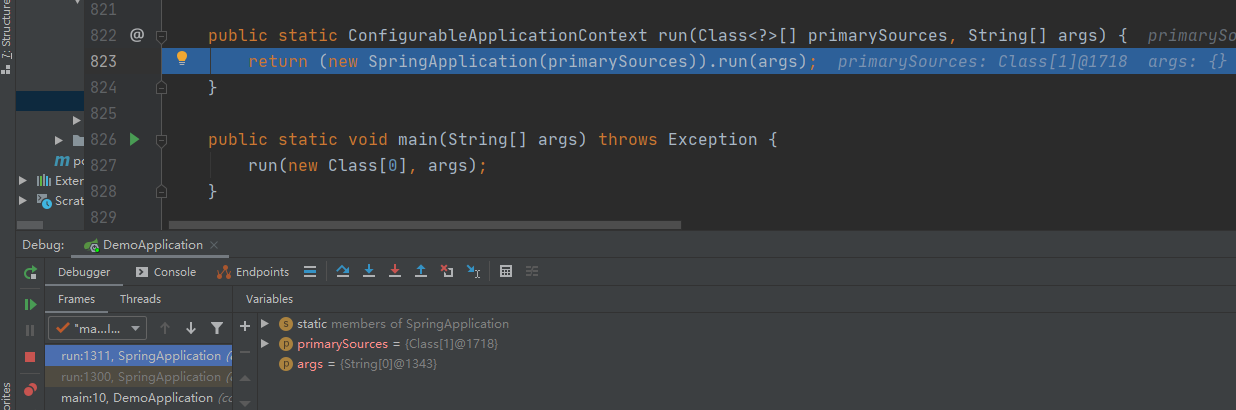
到这里会执行 new SpringApplication(primarySources)创建spring应用对象,继续F7往下跟会执行 SpringApplication构造器
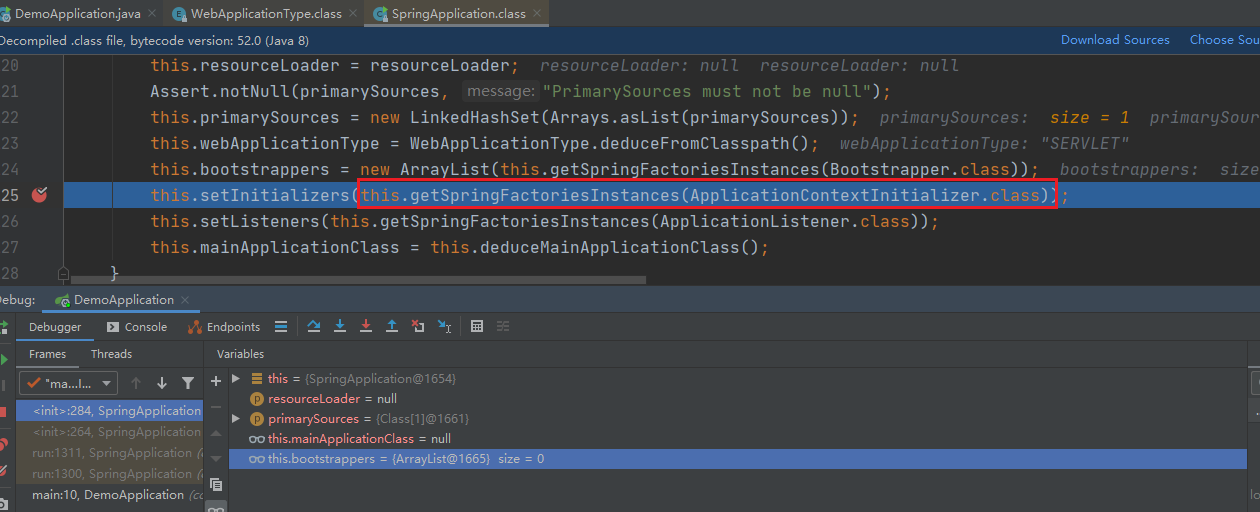
//SpringApplication构造器 public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { // 此处省略源码... // 资源加载器 this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); // 1.可能的web应用程序类型的类型。 this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class)); // 2.设置初始化应用context this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); // 3.设置初始化监听 this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); // 4.推演主程序类 this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass(); }很多不为人知的事情都是发生在这个对象初始化的时候,这里我们都来一一解密
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler", (ClassLoader)null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet", (ClassLoader)null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent("org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer", (ClassLoader)null)) { return REACTIVE; } else { String[] var0 = SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES; int var1 = var0.length; for(int var2 = 0; var2 < var1; ++var2) { String className = var0[var2]; if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, (ClassLoader)null)) { return NONE; } } // 这里是我们测试web容器 return SERVLET; } }1. 推断web 应用类型
这段代码是来推断我们的应用是哪种web应用程序
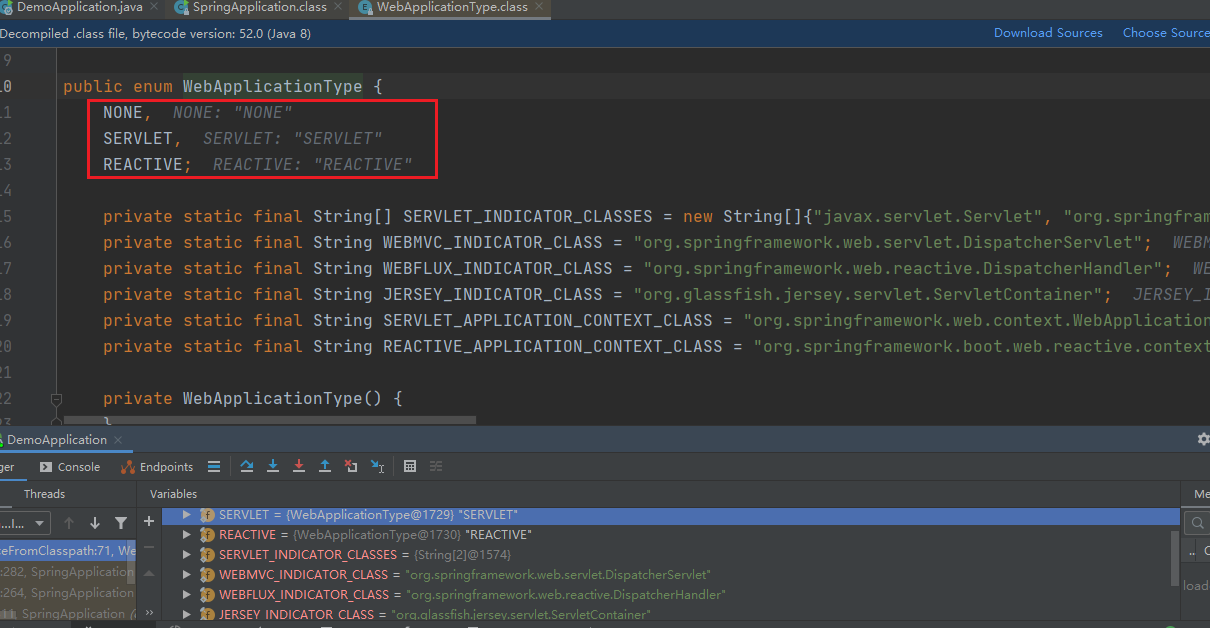
public enum WebApplicationType{ NONE,// 不是web应用 SERVLET,// servlet容器 REACTIVE; // 反应型web应用(webflux)}当然一开始我们加入了web的依赖,所以我们是 servlet 容器。
2. 初始化应用上下文
在设置初始化应用context的时候,是先执行了
getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)方法,参数是ApplicationContextInitializer.class字节码对象。
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against dupLicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet( // 加载ApplicationContextInitializer.class类型的类 // 这里传入就是参数 ApplicationContextInitializer.class SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); // 实例化加载到的类 List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); // 返回 return instances; }我们先来看看他是如何加载到这些类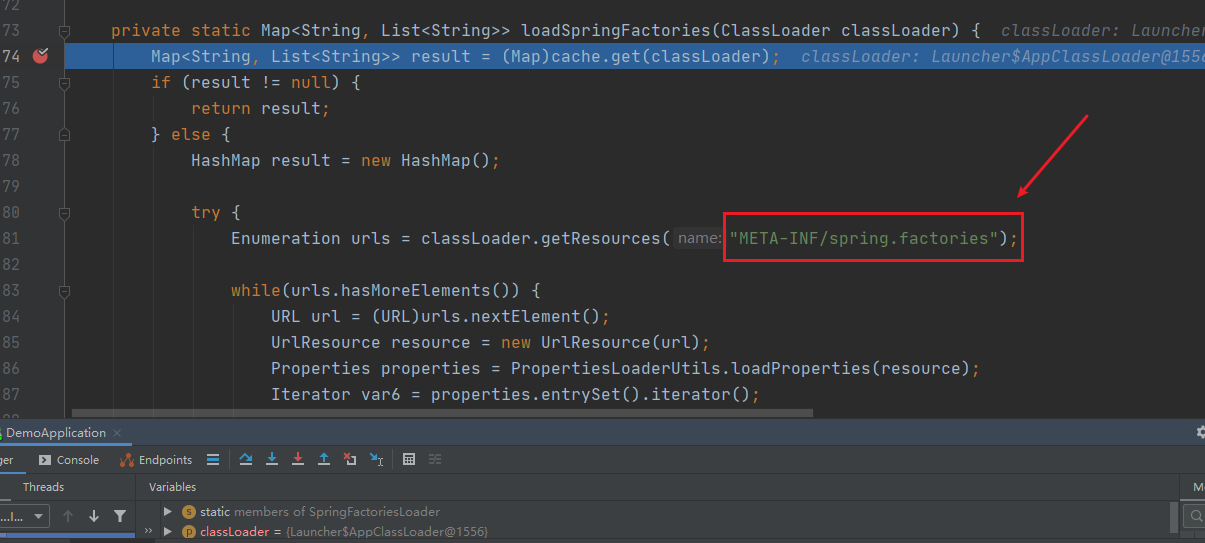
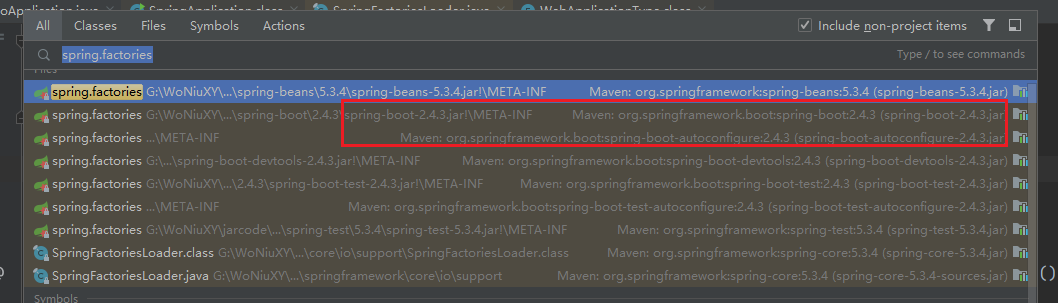
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) { // 从缓存中拿 Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { HashMap result = new HashMap(); try { // 从资源路径下加载 Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames; int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length; for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) { String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12]; ((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> { return new ArrayList(); })).add(factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> { return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)); }); cache.put(classLoader, result); // 返回所有的加载的类 return result; } catch (IOException var14) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14); } } }这里有两个加载配置类的地方其实都指向了META-INF/spring.factories,通过断点我们可以看到应用程序是加载了以下几个jar下的 spring.factories 文件。
双击Shifi搜索spring.factories可以看到它存在于以下工程中
spring-boot-2.4.3.RELEASE.jar 下的 spring.factories (截图未完整截取)
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.4.3.RELEASE.jar 下的 spring.factories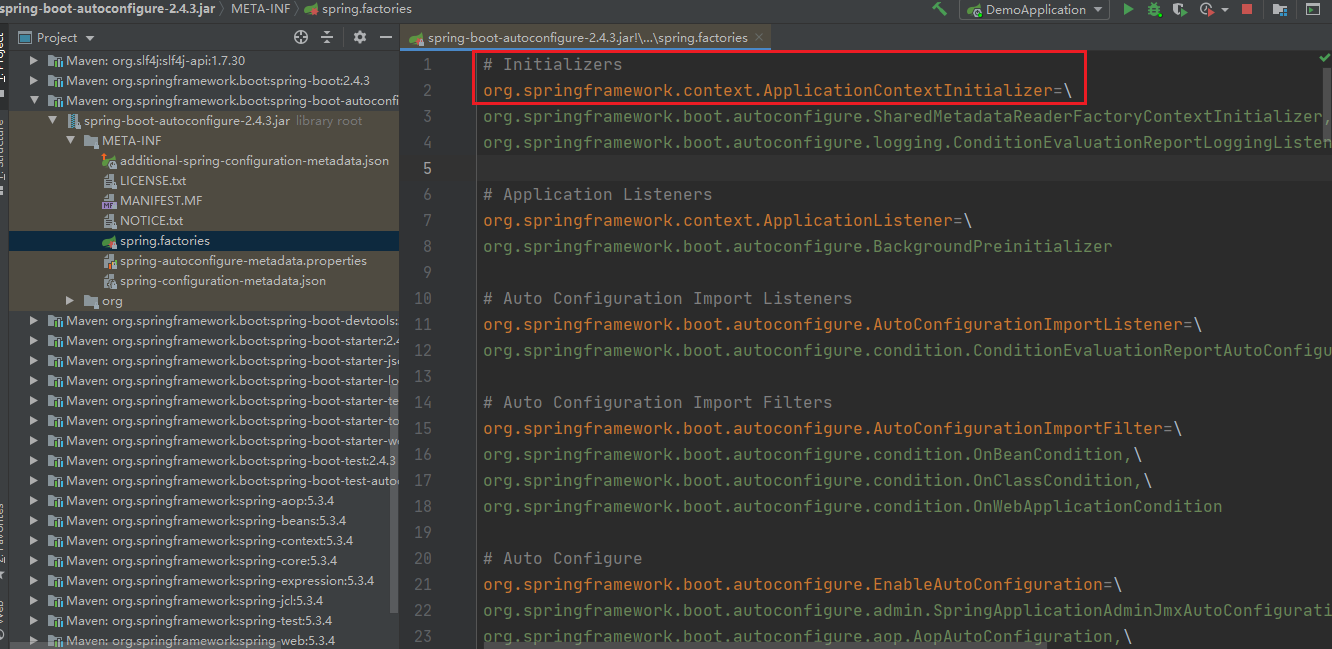
spring-beans-2.4.3.RELEASE.jar 下的 spring.factories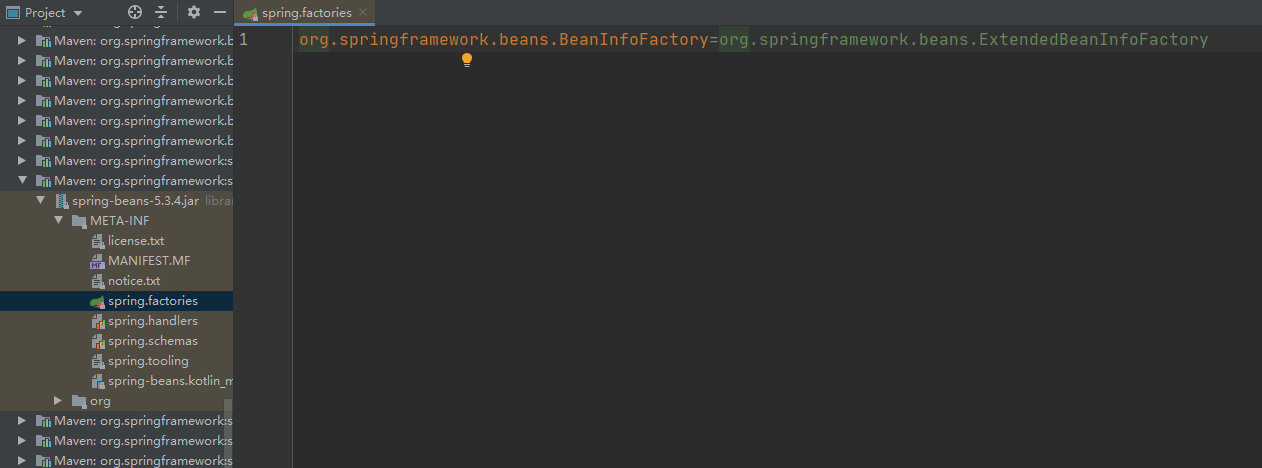
从Map中根据 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer 的类型拿到需要的类初始化类,断点进入 getOrDefault(factoryClassName,Collections.emptyList());方法
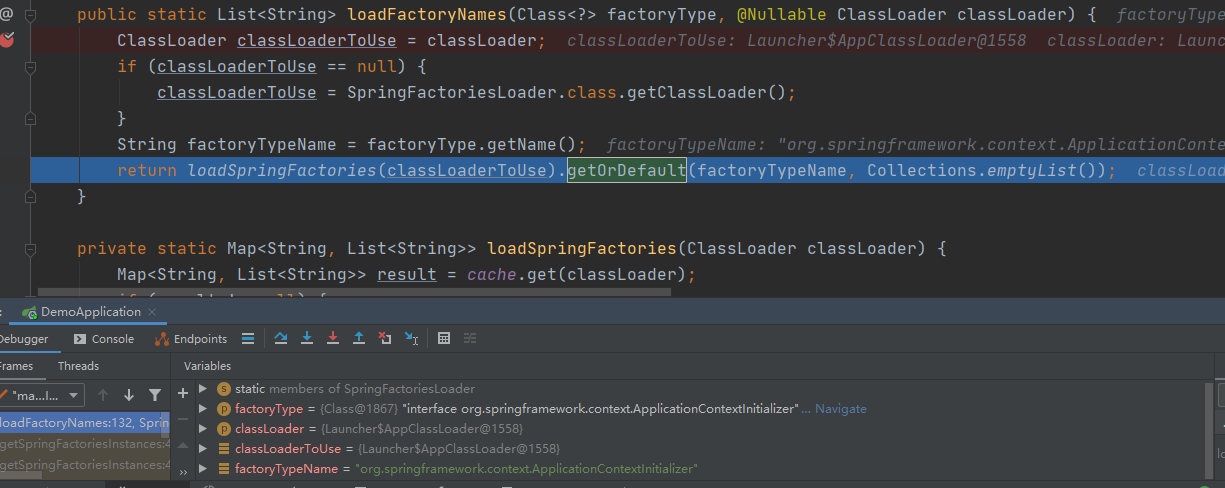
之后就是把加载到的需要初始化的类进行实例化添加到一个集合中等待备用
3. 初始化监听器类
最关键的的还是这句
当我们跟进去之后,会发现在初始化监听类的时候和上面初始化应用上下文是一样的代码。唯一不同的是 getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class))传进去的是·ApplicationListener.class 所以这里就不再赘述。
4. 推演主程序类
也就是这个最关键的代码了
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
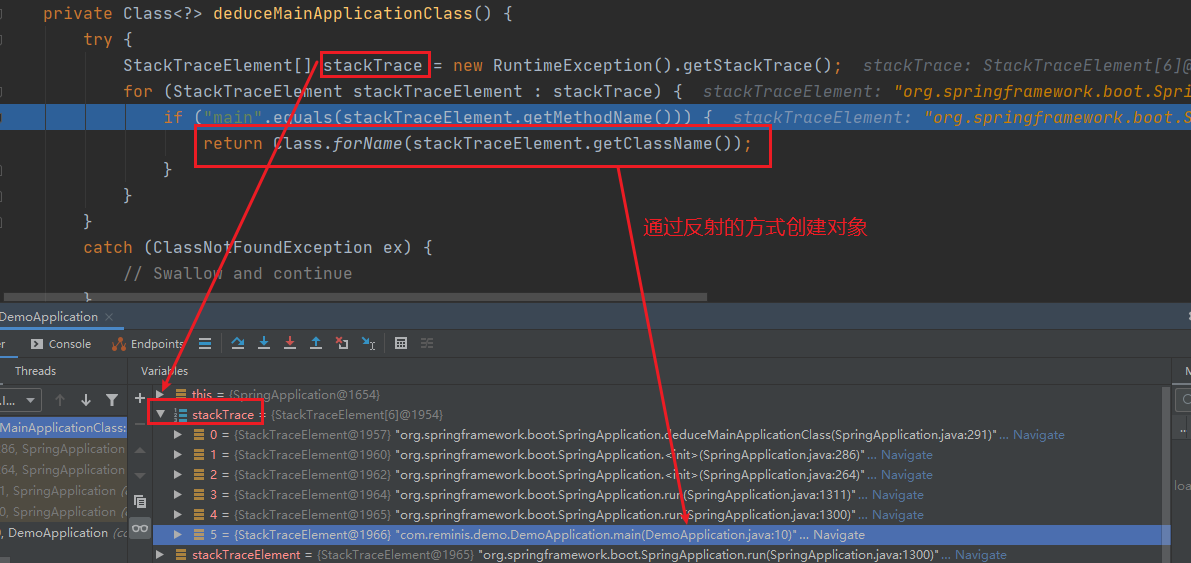
到这里就完成了SpringBoot启动过程中初始化SpringApplication 的过程。
这篇文章主要是给大家说了下SpringBoot 启动过程中初始化SpringApplication的流程,大致可以分为四个步骤∶
- 推演web应用的类型(如果没有加web依赖类型NONE)
- 初始化 ApplicationContextInitializer
- 初始化 ApplicationListener
- 推演出主程序类
通过这样四个步骤就完成了第一步 SpringApplication 的初始化过程。
原文转载:http://www.shaoqun.com/a/608600.html
优1宝贝:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1507
myyearbook:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/726
我们都知道SpringBoot自问世以来,一直有一个响亮的口号"约定优于配置",其实一种按约定编程的软件设计范式,目的在于减少软件开发人员在工作中的各种繁琐的配置,我们都知道传统的SSM框架的组合,会伴随着大量的繁琐的配置;稍有不慎,就可能各种bug,被人发现还以为我们技术很菜。而SpringBoot的出现不仅大大提高的开发人员的效率,还能避免由于"手抖"带
aca:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1371
naning9韩国官网:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2401
环球易购:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/1034
eDIS 关于"卖家正确使用SpeedPAK物流管理方案的实时情况"报告上线!:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/12687
后期维护小焦点:https://www.kjyunke.com/courses/102
亚马逊Prime Day期间,快收下这份低成本高效获取流量的小攻略!:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/131504
没有评论:
发表评论